Your guide to specialty
materials
Safety gloves are worn in thousands of work environments around
the world in various settings such as bakeries, hospitals and construction
sites. Simply put, safety gloves are protective clothing that provides
protection to the hands, fingers, thumbs, and wrists against external forces,
chemicals, the elements, and workplace hazards. For every industry that
requires safety gloves, there are dozens of different items that offer
specialty specifications for the wearer's needs. In this era of rapid
technological advances, new chemicals are being developed and processes are
being developed. In many ways, workers are exposed to greater risks in their
work environment and having the right safety equipment is important.

Materials
HPPE (High
Performance Polyethylene)
HPPE fiber
has an extremely high resistance to physical-mechanical disturbances from the
external environment, it is also flexible and light, but very durable. Gloves
made entirely of HPPE can typically achieve cut resistance at level 3 / B
according to EN388:2016, but when reinforced with steel or other fiber this can
be increased to cut resistance at level 5 / E and higher .
FIBER GLASS
High
strength to weight ratio and flexibility. Fiberglass is a lightweight material
that creates strength in almost any finished product or component. Fiberglass
can be stronger than steel and metals. Very resistant to the extremes of the
environment, that is why it is used in anti-cut gloves. It has a smooth, silky
surface that feels cool to the wearer, offering high comfort to the user.
Fiberglass can be used as a single component to provide shear strength,
typically reaching level 3 / B, but also to reinforce other fibers.
STEEL FIBER
Compared to
other types of fibers such as carbon, glass, aramid or natural fibers, metallic
fibers have a low electrical resistance. This makes them suitable for any
application that requires electrical conductivity. Their excellent thermal
resistance makes them withstand extreme temperatures. Corrosion resistance is
achieved by using high quality alloys in stainless steels or other metals.
Other advantageous mechanical properties of metallic fibers include high
deformation, ductility, shock resistance and fire resistance. Stainless steel
is commonly used to provide cut resistance in combination with other fibers
such as aramid or HPPE. Cut resistance with steel has been and continues to be
a preferred option for the user,
PolyKor®
PolyKor® Xrystal® is an engineered thread that represents the next
generation in maximum cut protection and comfort. It is a blend of high modulus
polyethylene and mineral based fibers. These mineral-based fibers have a
similar chemical composition to glass, but are inherently better in terms of
resistance to cutting and oxidation, as well as compression and shear.
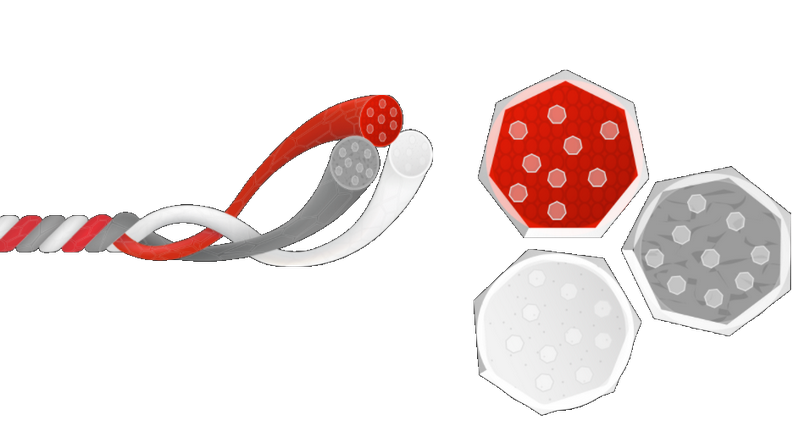
.Continuous fiber is produced by ingenious extrusion from mineral
melts, creating one of the strongest and toughest fibers in the world.
CARBON FIBER
Antistatic
gloves are made of conductive carbon fibers and coatings that prevent the
build-up of static electricity that, when discharged, can damage sensitive
equipment or create dangerous sparks. Carbon fibers are extremely stiff, strong
and lightweight and are used in many processes to create excellent construction
or protective materials. The properties of carbon fiber are close to that of
steel, and the weight is close to that of plastic. Thus, the strength-to-weight
ratio (as well as the stiffness-to-weight ratio) of carbon fiber is much higher
than that of steel or plastic. Carbon fiber is extremely strong.
Glove covers
Nitrile foam
A layer of
foamed nitrile acts as a sponge when working with oily surfaces, providing
excellent grip in wet and oily conditions. The nitrile in the foam also allows
the hand to breathe, which means increased comfort for wearers. With the open
pore structure of flexible foam nitrile, it can become saturated, so it is more
suitable for oily conditions and dry surfaces.
Fine
textured nitrile
Gloves with
a fine layer of nitrile are tough and durable with good abrasion and puncture
resistance. They typically have a good grip on areas with oil, grease and
liquids, however, they may offer less dexterity, so they are not suitable for
complicated assembly work. Fine nitrile coated gloves work well in a number of
industries including automotive, glass manufacturing, metal fabrication or
stamping and construction.
Polyurethane
(PU)
PU is often
considered the ideal coating for cut protection gloves due to its soft and
stretchy properties that still provide good puncture resistance without being
too bulky. PU coatings tend to have higher levels of penetration into the knit
lining as a disadvantage and this can cause skin sensitivity issues. PU is also
a non-breathable coating, so it is often used as a finger or palm-only coating
style to reduce sweat inside the gloves. PU is durable and flexible, making it
an excellent coating for general sharps handling and assembly in many
industries such as manufacturing, aerospace and precision handling.
Latex
Latex offers
high elasticity and grip compared to other glove coatings. This is especially
true of rough-textured latex, which offers remarkable adhesion often along
puncture resistance. A downside to latex-coated gloves is that latex contains a
protein that can sometimes cause allergic reactions in some wearers. But, latex
is very durable and is still ideal for a number of applications in industries
such as construction, glass, utilities and waste management.
Polyvinyl Chloride
(PVC)
Polyvinyl
chloride (PVC) is a thermoplastic polymer. PVC offers good abrasion resistance
but can be susceptible to punctures, cuts and jams. Although flexible, it does
not offer the tactile sensitivity associated with most rubber products. PVC
begins to soften at about 82°C. PVC is effective against water and most aqueous
solutions, detergents and diluted bases and acids. It has only limited chemical
resistance to organic solvents. PVC is one of the most common coatings for work
gloves.
Thermoplastic
Rubber (TPR)
TPR material, also known as thermoplastic rubber, is a material
that has both plastic and rubber properties. It is lightweight and has good
abrasion resistance, tear resistance, weather resistance and electrical
properties.
Features of TPR material
· It has high flexural fatigue
strength
· High
resistance to tearing and abrasion
· It has high
impact resistance and good dielectric properties
· Resistant to
chemicals
· Recyclable
· It can be
used at temperatures between -30°C and 140°C
Features of TPR material



